Sindrom Wolff Parkinson White

The heartbeat is controlled by electrical signals that move through the heart in a highly coordinated way.
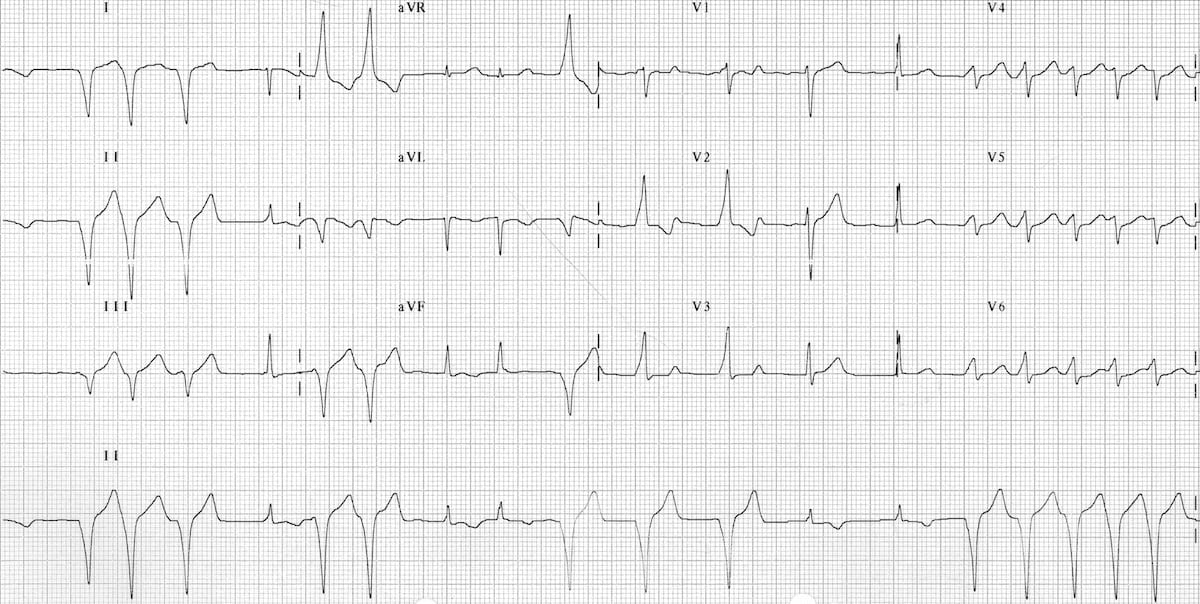
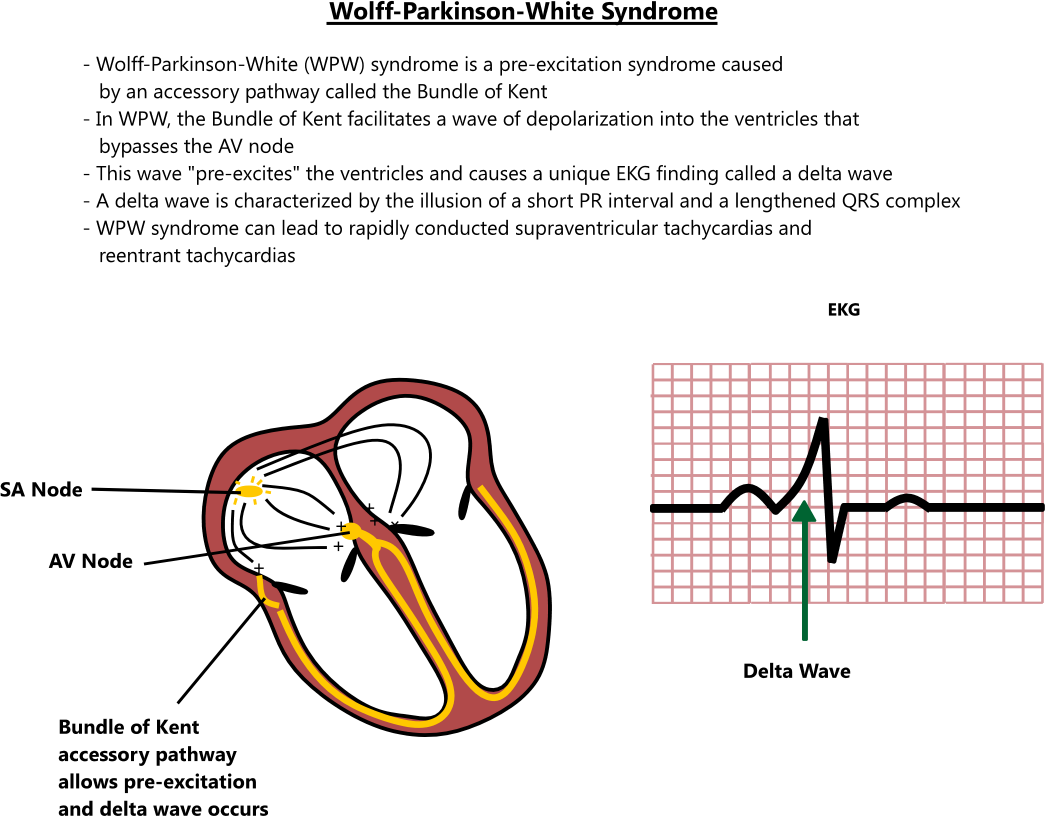
Sindrom wolff parkinson white. Wpw causes 100 or more heartbeats per minute. About 40 of people with the electrical problem never develop symptoms. Wolff parkinson white syndrome is a condition characterized by abnormal electrical pathways in the heart that cause a disruption of the heart s normal rhythm arrhythmia. A normal heartbeat is about 60 to 100 beats per minute.
Symptoms can include an abnormally fast heartbeat palpitations shortness of breath lightheadedness or syncope. Normally electrical signals in the heart go through a pathway that helps the heart beat regularly. Síndrome de wolff parkinson white wpw el sindrome de wolff parkinson white es una afección en la cual existe una ruta eléctrica adicional del corazón que lleva a períodos de frecuencia cardíaca rápida taquicardia. Este síndrome es una de las causas más comunes de problemas de frecuencia cardíaca rápida en bebés y niños.
In 1933 other doctors noted the reason for this irregular rhythm was a faster passage of impulses traveling through the ventricles. A specialized cluster of cells called the atrioventricular node. Wolff parkinson white wpw syndrome is a condition that causes tachycardia fast heartbeat. Wolff parkinson white syndrome is caused by having an extra pathway in the heart that causes a very rapid heart rate.
Wolff parkinson white syndrome wpws is a disorder due to a specific type of problem with the electrical system of the heart which has resulted in symptoms. Sindromul wolff parkinson white wpw este o malformatie congenitala care implica prezenta unui tesut conductiv anormal intre atrii si ventricule care este asociat frecvent cu instalarea tahicardiei supraventriculare. Wolff parkinson white syndrome is a congenital heart defect something you re born with. In 1944 doctors confirmed the presence of extra pathways.
The condition which is present at birth is fairly rare. But most times it happens randomly and doesn t run in families. In 1930 wolff parkinson and white described a distinct electrocardiograph ecg pattern in healthy young people with short bursts of tachycardia. The electrical pathway of the heart prevents extra beats from occurring and keeps the next beat from happening too soon.
Parents can pass it down to their children.